
Hard Skills vs Soft Skills - Understanding the Balance

29 January, 2025
Share this article
Table of Contents
The work environment today is dynamic and competitive. To succeed, it’s not only a matter of what you know, but how you apply it as well.
First, you have the hard skills, which are the technical abilities and knowledge required to perform specific tasks. They are the foundation for excelling in any role.
Afterwards, you have the soft skills. They are interpersonal and behavioral skills. They influence how you communicate, collaborate and interact with people around you, from colleagues to clients and any other person.
While hard skills help you meet the technical requirements of a job, soft skills enable you to thrive and collaborate with others, building relationships and trust while you navigate challenges.
What are soft skills?
Soft skills are personal, non-technical abilities that influence how individuals interact with others, manage relationships, and navigate their environments. They include traits like communication, teamwork, adaptability, and emotional intelligence, which enable effective collaboration and problem-solving.
Unlike hard skills, which are specific and measurable, soft skills are more interpersonal and behavioral, making them essential for building connections, fostering trust, and succeeding in both professional and personal settings.
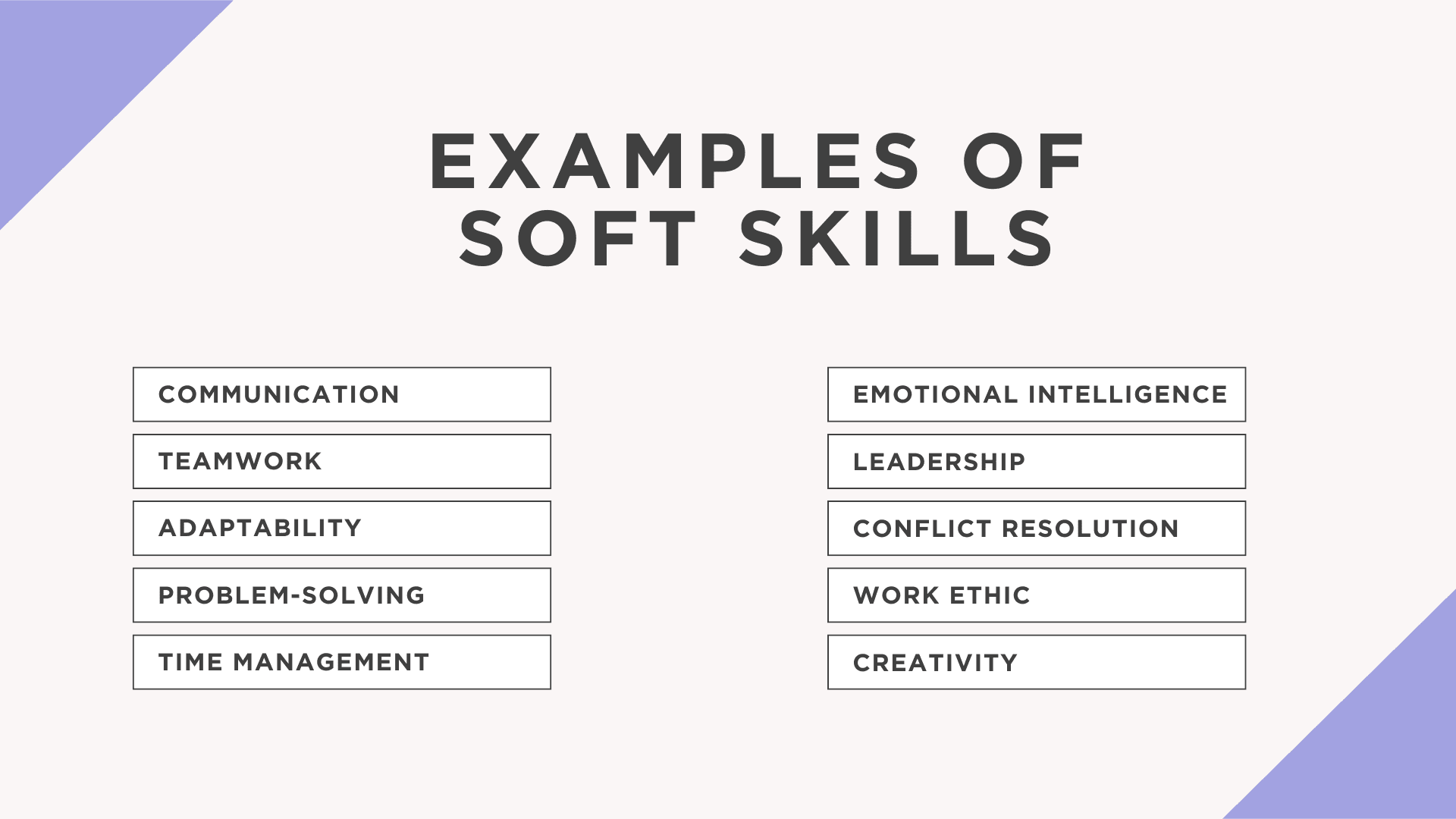
Examples of Soft Skills
- Communication: The ability to convey ideas clearly, listen actively, and adapt messages to different audiences. One example here would be the ability to give and receive constructive feedback.
It is important to mention that certain personality traits can help out with communication. Being an extrovert is an amazing personality trait to have in this case. However, introverts can also be excellent communicators by leveraging their active listening and thoughtful communication styles. - Teamwork: Collaborating effectively with others to achieve common goals, such as respecting a deployment deadline or delivering the best pitch to a client.
- Adaptability: Adjusting to changing circumstances, roles, or environments with ease. This is a critical soft skill in startups, where you need to change the plan, make fast changes to a website or be quick in updating proposals in sales.
- Problem-Solving: Thinking critically and creatively to identify solutions to challenges such as when a provider misses a deadline, your cameraman doesn’t wake up for a photoshoot or simply when you need to mop up after that one specific colleague.
- Time Management: Organizing and prioritizing tasks to meet deadlines efficiently. Also, this skill enables you to better understand which tasks are taking too much time, helping you decide to remove some tasks, improve them or delegate them.
- Emotional Intelligence: Understanding and managing one’s emotions while empathizing with others. This is the skill to have. Especially when being a leader.
- Leadership: Inspiring, guiding, and motivating others to achieve shared objectives, usually through putting your team above yourself and showing that you care and can work alongside others. Effective leadership skills are the sure way in building your team.
- Conflict Resolution: Addressing and resolving disagreements constructively, without minimizing someone's feelings or taking sides.
- Work Ethic: Demonstrating reliability, responsibility, and a commitment to high standards, especially when working with clients or colleagues.
- Creativity: Thinking outside the box to develop innovative ideas and solutions, such as a new guerilla marketing strategy or coming up with new functionalities for your app.
What are hard skills?
Hard skills are specific, technical abilities or knowledge that are measurable, teachable, and directly related to performing a particular task or job. These skills are often acquired through formal education, training programs, certifications, or on-the-job experience.
Unlike soft skills, which are interpersonal and behavioral, hard skills are more tangible and task-oriented, making them easier to quantify and evaluate.
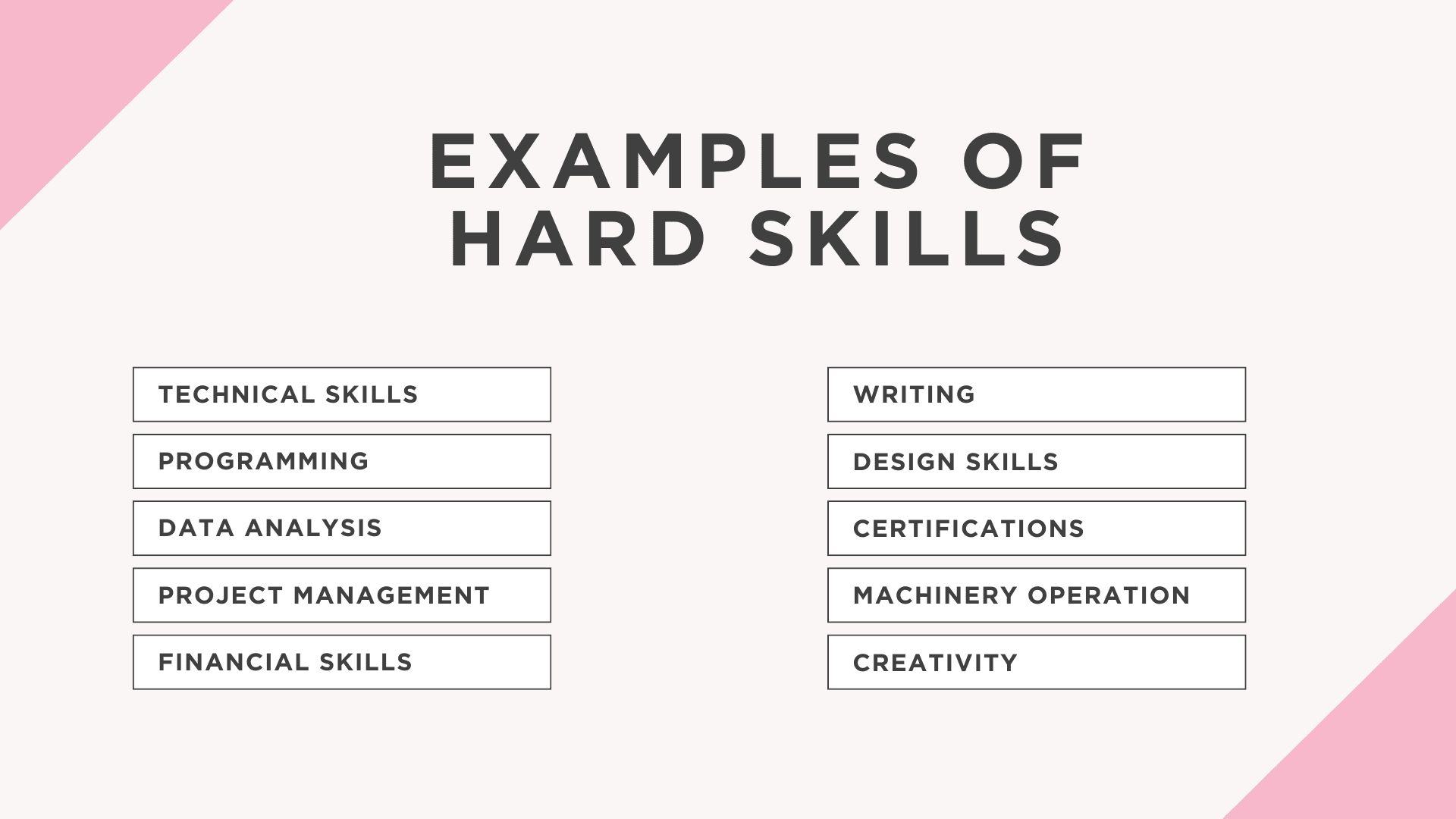
Examples of Hard Skills
- Technical Skills: Proficiency in tools or software like Microsoft Excel, AutoCAD, Photoshop, or SQL.
- Programming: Knowledge of programming languages such as Python, Java, C++, or HTML.
- Foreign Languages: Fluency in languages like Spanish, French, or Mandarin.
- Data Analysis: Experience with tools like Tableau, Power BI, or statistical analysis using R or Python.
- Project Management: Using methodologies like Agile, Scrum, or tools like Jira and Trello.
- Financial Skills: Budgeting, forecasting, accounting, or using tools like QuickBooks.
- Writing: Technical writing, content creation, or grant proposal writing.
- Design Skills: Graphic design, UX/UI design, or knowledge of tools like Figma and Adobe Creative Suite.
- Certifications: Holding credentials such as Certified Public Accountant (CPA), Six Sigma, or AWS Certified Solutions Architect.
- Machinery Operation: Operating heavy machinery, equipment, or specialized tools in manufacturing or construction.
One way of proving your hard skills is to have a professional certificate for that specific skill. Be it a diploma from college or a professional certificate from a course platform like Udemy, certifications are a sure way to prove your worth, especially if you add skills on your resume, where your potential employers need to find about you without meeting you in person.
Difference between hard and soft skills
Hard skills and soft skills are fundamentally different in their nature and application, yet both are essential for professional success. Hard skills are specific, teachable abilities or technical knowledge required to perform a particular job.
These skills are often acquired through formal education, training programs, or certifications and are measurable and task-oriented. Examples of hard skills include programming, data analysis, operating machinery, or fluency in a foreign language. They are usually assessed through tests, portfolios, or performance evaluations.
On the other hand, soft skills are personal and interpersonal traits that affect how individuals interact with others and navigate their work environment. These skills, such as communication, teamwork, problem-solving, and emotional intelligence, are less tangible and harder to measure. Soft skills are developed through life experiences, self-awareness, and social interactions, and they are critical for effective collaboration, leadership, and adaptability in the workplace.
The Importance of Balancing Hard and Soft Skills
Balancing hard and soft skills is crucial for success in today’s professional environment, as both skill sets play complementary roles in achieving goals. Hard skills provide the technical knowledge and expertise necessary to perform specific tasks, such as coding, financial modeling, or operating machinery.
These skills are often what employers look for when hiring, as they are essential for meeting job requirements. However, technical proficiency alone is not enough to thrive in a workplace. Soft skills, such as communication, teamwork, and adaptability, are what enable individuals to apply their hard skills effectively in a collaborative and dynamic setting.
When hard and soft skills are balanced, professionals can perform their tasks efficiently while fostering positive relationships and contributing to team success. For instance, a project manager with strong organizational skills (hard skill) who also communicates clearly and motivates their team (soft skills) is far more effective than one who lacks interpersonal abilities.
Similarly, employees with technical expertise but no ability to work in a team or resolve conflicts may struggle to achieve long-term success.
By combining technical mastery with interpersonal finesse, individuals can adapt to diverse situations, build trust, and excel in both technical and leadership roles. This balance is not just beneficial for individuals but also enhances organizational performance, creating a productive and harmonious work environment.
How to develop hard skills?
Developing hard skills is an essential step in building technical expertise and enhancing your career prospects. Hard skills are specific, measurable abilities acquired through education, training, and practice. They are critical for performing specialized tasks and meeting job requirements. Here are effective ways to develop hard skills:
- Pursue Formal Education
Enrolling in relevant courses or academic programs is one of the most effective ways to gain hard skills. Degrees, diplomas, and certifications provide a structured curriculum that equips you with the necessary technical knowledge and qualifications for specific industries or roles. - Attend Workshops and Training Programs
Short-term workshops, bootcamps, and training sessions offer targeted learning opportunities to develop specific hard skills, such as coding, graphic design, or project management. These programs are often industry-focused and provide hands-on experience. - Obtain Certifications
Earning certifications in your field validates your expertise and makes you more competitive in the job market. Certifications such as PMP (Project Management Professional), AWS Certified Solutions Architect, or Microsoft Excel Specialist demonstrate your proficiency in specific tools and methodologies. - Practice and Apply Skills
Practical experience is key to mastering hard skills. Engage in projects, internships, or volunteer work where you can apply your knowledge in real-world settings. For example, a budding graphic designer could create a portfolio of design projects to refine their skills. - Utilize Online Resources
The internet is a valuable tool for learning hard skills. Platforms like Coursera, Udemy, LinkedIn Learning, and Khan Academy offer courses on various topics, often with the flexibility to learn at your own pace. Many platforms also provide certifications upon completion. - Stay Updated with Industry Trends
Hard skills can become outdated in fast-changing industries like technology and healthcare. Regularly updating your knowledge by reading industry publications, attending webinars, or joining professional networks ensures you remain competitive and relevant. - Leverage Mentorship and Networking
Working with mentors or experienced professionals in your field can help you gain insights and practical advice on developing technical expertise. Networking with peers and industry leaders also opens opportunities to learn new tools and practices.
How to develop soft skills?
Developing soft skills is essential for fostering strong relationships, effective communication, and adaptability in both personal and professional settings. Unlike hard skills, soft skills are less tangible and are often honed through experience, practice, and self-awareness. Here are effective ways to develop soft skills:
- Practice Active Listening
Active listening involves fully concentrating on what others are saying, understanding their perspectives, and responding thoughtfully. To improve this skill, focus on the speaker, avoid interruptions, and ask clarifying questions to ensure you comprehend their message. - Seek Feedback
Ask colleagues, mentors, or friends for constructive feedback on how you interact with others. Honest feedback helps identify areas for improvement, such as communication, teamwork, or emotional intelligence, and provides guidance on how to enhance these skills. - Participate in Team Projects
Working in teams allows you to develop essential soft skills like collaboration, conflict resolution, and adaptability. Engage actively in team discussions, take on different roles, and observe how others approach challenges to refine your interpersonal abilities. - Build Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence involves understanding and managing your emotions while empathizing with others. Develop this skill by practicing self-awareness, regulating your emotional reactions, and seeking to understand others' feelings and perspectives in various situations. - Improve Communication Skills
Practice clear and concise verbal and written communication. Engage in public speaking, join a debate group, or attend workshops to enhance your ability to articulate ideas effectively. Pay attention to body language and tone, as nonverbal cues are also vital in communication. - Expand Your Comfort Zone
Challenging yourself to step out of your comfort zone helps build confidence and adaptability. Take on tasks or roles that require interacting with new people, learning new processes, or managing unfamiliar situations. - Join Networking Events and Workshops
Participate in professional networking events, soft skills training workshops, or volunteering opportunities. These experiences provide valuable chances to practice social skills, meet new people, and adapt to diverse environments. - Read and Learn
Books, podcasts, and online courses on topics like leadership, communication, or emotional intelligence can provide insights and strategies for developing soft skills. Reading self-help and personal development literature can also enhance your understanding of these skills. - Be Open to Change and Feedback
Soft skills often improve when you remain open to learning and adapting. Reflect on past interactions, identify areas for growth, and implement changes to improve how you collaborate and communicate. - Observe and Learn from Others
Pay attention to individuals who excel in soft skills. Observe how they handle conflicts, communicate ideas, or lead teams. Emulating positive behaviors can accelerate your development.
The Role of Employers in Nurturing a Balance Between Hard and Soft Skills
Employers play a critical role in fostering a workforce that balances hard and soft skills. While technical expertise is essential for meeting job-specific demands, interpersonal abilities like communication, teamwork, and adaptability are equally vital for creating a cohesive and productive work environment.
Organizations that prioritize the development of both skill sets not only enhance employee performance but also position themselves for long-term success in a competitive landscape.
One of the most effective ways employers can nurture this balance is by offering comprehensive training programs. Hard skills training can include workshops, certifications, and on-the-job technical instruction, while soft skills training can focus on areas like leadership, conflict resolution, and emotional intelligence.
Employers can also promote mentorship programs where experienced professionals share insights on technical tasks and interpersonal strategies, helping employees grow holistically.
In addition to training, employers should integrate hard and soft skills assessment into their hiring and performance evaluation processes. This ensures that candidates and employees are recognized not only for their technical abilities but also for their capacity to collaborate and communicate effectively.
Creating a culture that values both skill sets encourages employees to invest in their personal and professional development, ultimately strengthening the organization as a whole.
By actively supporting the development of both hard and soft skills, employers can build a well-rounded workforce equipped to meet technical challenges while fostering collaboration and innovation. This balanced approach drives employee satisfaction, team synergy, and organizational growth.
Career
Keep up to date with our most recent articles, events and all that Pluria has to offer you.
By subscribing to the newsletter you agree with the privacy policy.

In the last two years I’ve been working remotely from over 20 countries but no part of the world compares to Latin America: countries and cultures spreading over two continents with climates[...]
04 December, 2023

A massive move to hybrid work
In 2022, 60% of companies will switch to a hybrid working model, and a third of them will fail on their first attempt to work from anywhere, Forrester p[...]
04 December, 2023

When the employees in the most innovative company on the planet rally against their CEO because he wants them back in the office three days a week, it is a sign that it is not enough to be innovative in tec[...]
04 December, 2023